Digital Transformation Consulting: Cost, Strategy,...
October 13, 2025

Elasticsearch is a popular open-source search and analytics engine that is built on Apache Lucene. Elasticsearch is a highly scalable, distributed RESTful search and analytics engine designed for horizontal scalability, reliability, and easy management. It allows storing, searching, and analyzing big volumes of data quickly and in near real-time.
Elasticsearch is a powerful and versatile search and analytics engine that excels in handling large volumes of data. One of the key aspects of optimizing Elasticsearch performance is the thoughtful configuration of shards, which are the fundamental units for data distribution and parallel processing. In this document, we explore the benefits and steps for increasing the number of shards in Elasticsearch to achieve better performance, particularly when dealing with substantial datasets.
Shards are the building blocks of Elasticsearch indices, and they play a pivotal role in achieving efficient data distribution and parallelism across a cluster. By increasing the number of shards in your Elasticsearch setup, you can harness several benefits:
Also Read: Explore Elasticsearch and Why It’s Worth Using?
For testing this we hit the same Elastic Search Query in 2 indexes first with one shard and another with 3 shards. By this, we noticed that the response time is boosted to a great extent.
Settings of index:

Search output:
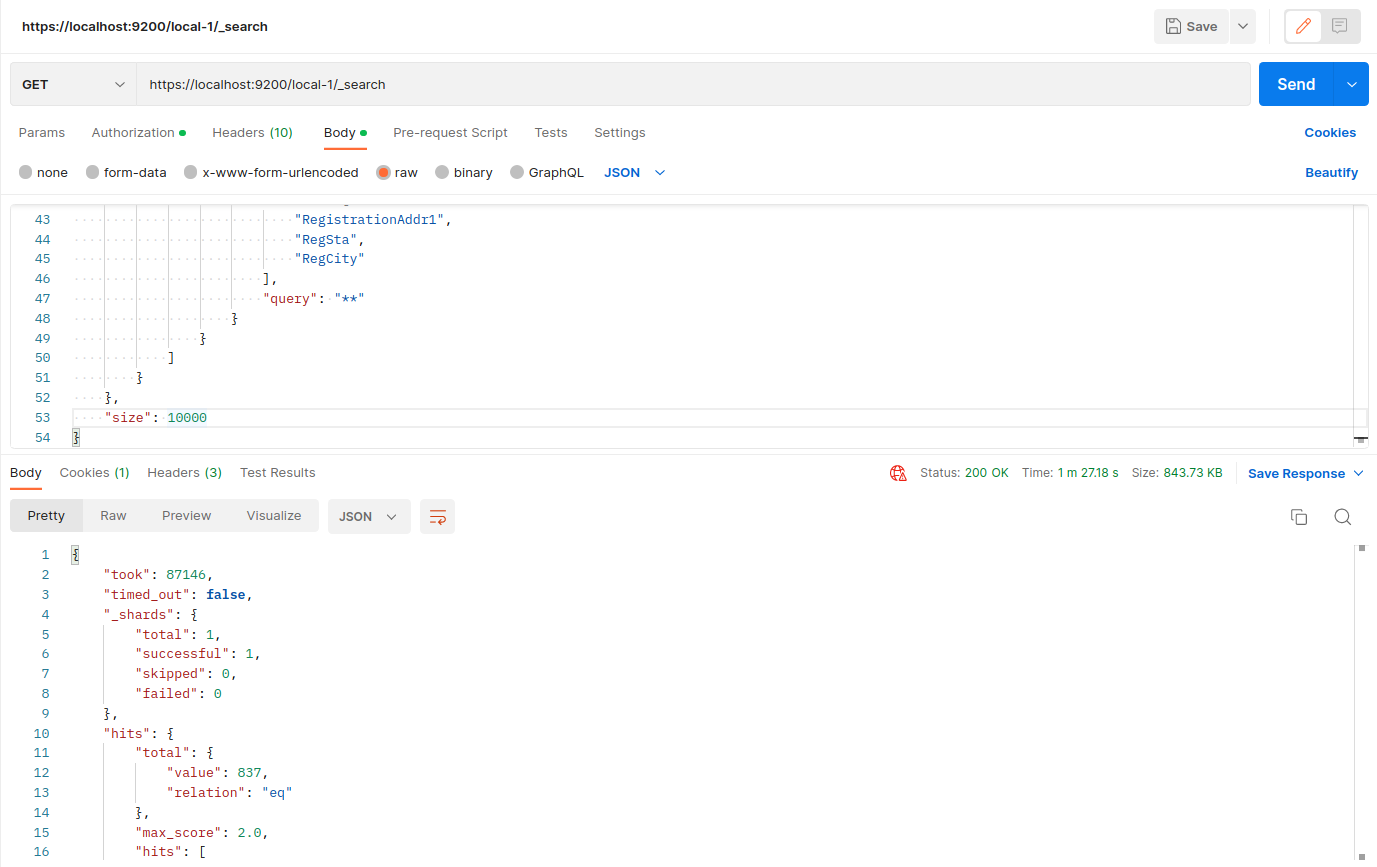
Response Time: 1m 28s
Settings of index:

Search output:
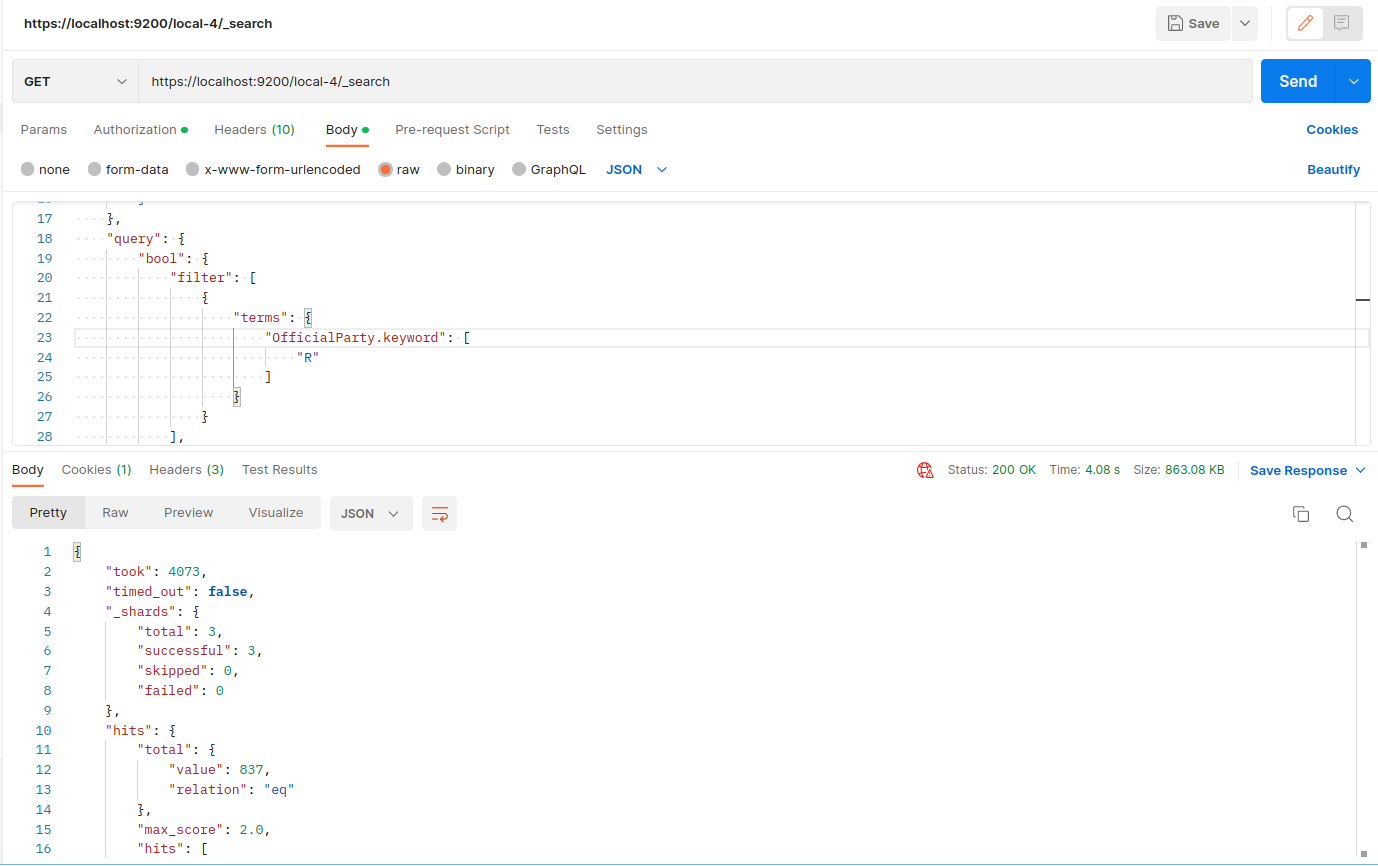
Response Time: 4s
The recommendation is to adjust the max_open_scroll_context setting of the Elasticsearch cluster. This setting controls the maximum number of open scroll contexts across the cluster. Scroll contexts are crucial for scrolling through a large number of search results while consuming system resources, particularly memory.
The search.max_open_scroll_context setting in Elasticsearch controls the maximum number of scroll contexts that can be opened at the same time per node.
Also read: Google Cloud & Elasticsearch: Interactive Search Intro
By setting this limit, you can control resource usage and prevent the system from being overwhelmed with too many open scroll contexts. This is particularly important in scenarios where you have a large number of concurrent scrolling searches.
For example, if you set max_open_scroll_context to 500, Elasticsearch will allow up to 500 open scroll contexts for that index. Once the limit is reached, you won’t be able to open additional scroll contexts until some of the existing ones are closed.
curl -x “” -X PUT localhost:9200/_cluster/settings -H ‘Content-Type: application/json’ -d'{
“persistent” : {
“search.max_open_scroll_context”: 1024
},
“transient”: {
“search.max_open_scroll_context”: 1024
}
}’
Firstly, with default search.max_open_scroll_context this was the result for 13 lakhs+
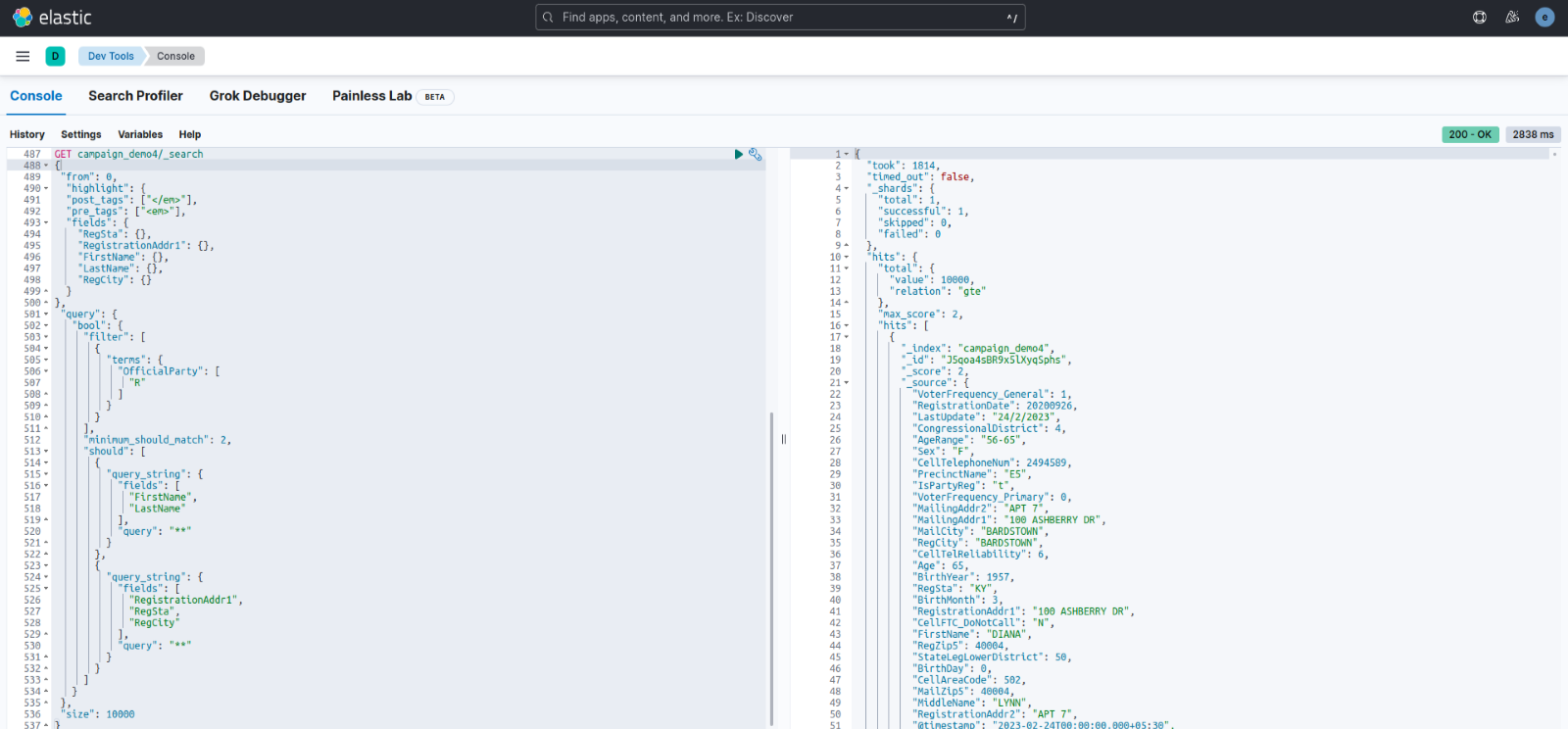
Response time: Around 1900ms
After updating the search.max_open_scroll_context to 500 this was the result:
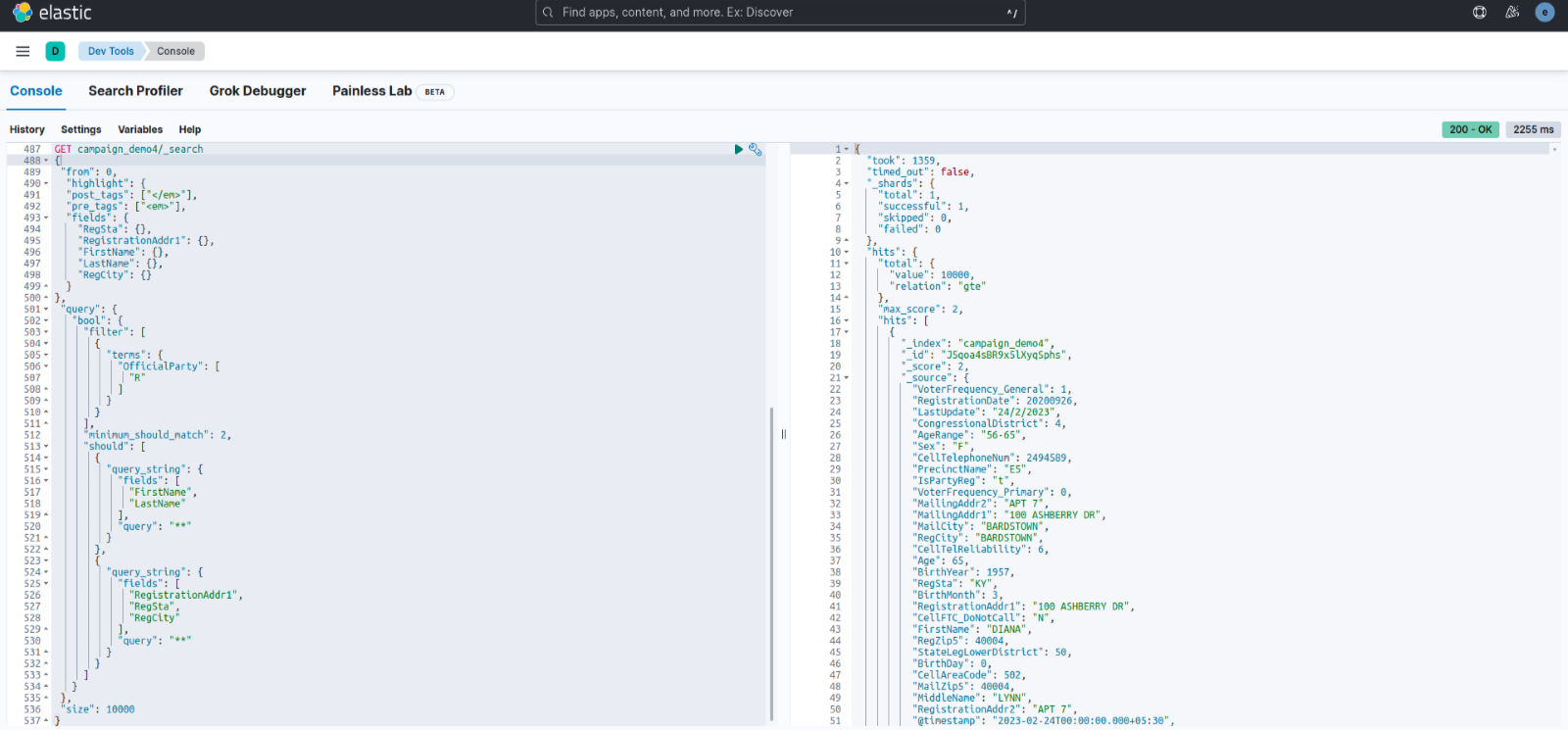
Response time: Around 1370ms
After updating the search.max_open_scroll_context to 1024 this was the result:
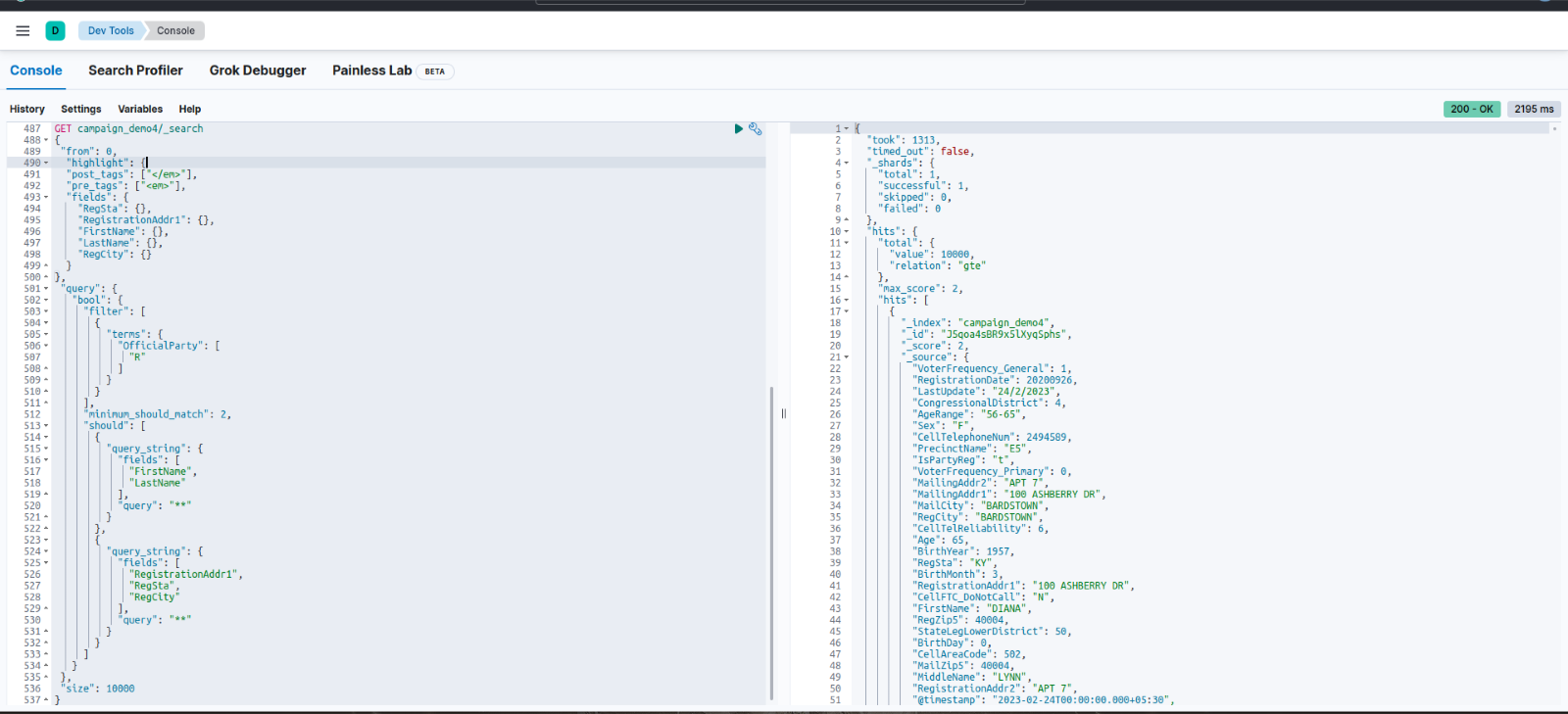
Response time: Around 1300ms
Asynchronous search lets you search requests that run in the background. You can monitor the progress of these searches and get back partial results as they become available. After the search finishes, you can save the results to examine at a later time.
In this, we can use asyn_search API instead of search API. This optimizes the search result. But the Asyn search doesn’t guarantee results every time sometimes it results in no response. So this isn’t an optimal approach.
Suggestions:
Here are some suggestions to optimize the performance of the Elasticsearch query