Python Kafka Integration Event Driven Architecture with Producers & Consumers (2025 Guide)
By Mahipalsinh Rana February 19, 2024
Why Python + Kafka Is a Powerful Combination
Python is widely used for APIs, data pipelines, analytics, and automation, while Kafka provides durable, scalable, distributed messaging.
Together, they enable modern enterprise software development patterns such as real-time data streaming and asynchronous system decoupling
- Real-time data streaming
- Event-driven microservices
- Asynchronous system decoupling
- High-throughput data ingestion
- Fault-tolerant processing
Common enterprise use cases:
- Payment events
- Activity logs
- IoT telemetry
- Data lake ingestion
- ML feature pipelines
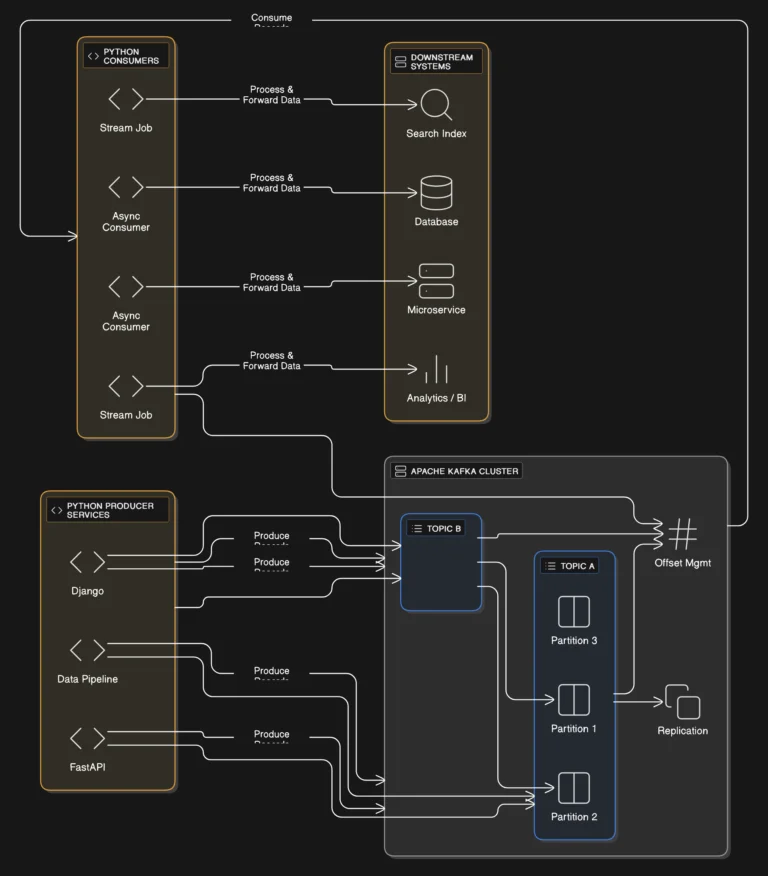
Python Kafka Architecture Overview
A typical Python–Kafka architecture consists of:
- Python Producers
FastAPI apps, Django services, batch jobs, or data pipelines publishing events. - Kafka Cluster
Brokers managing topics, partitions, replication, and durability. - Python Consumers
Async services or workers consuming messages independently at scale. - Downstream Systems
Databases, microservices, analytics platforms, search engines, or BI tools deployed using Cloud & DevOps best practices - Monitoring & Governance
Offset tracking, lag monitoring, retries, and failure handling.
Building Kafka Producers in Python
Producers publish messages to Kafka topics. Python supports Kafka via multiple libraries.
Kafka producers are commonly implemented as part of scalable Backend Engineering architectures handling high-volume event ingestion
Popular Libraries
- kafka-python
- confluent-kafka
- aiokafka (async)
Correct Practice:
from kafka import KafkaProducer
import json
producer = KafkaProducer(
bootstrap_servers='localhost:9092',
value_serializer=lambda v: json.dumps(v).encode('utf-8')
)
producer.send('orders', {'order_id': 123, 'status': 'created'})
producer.flush()
Best Practices
- Use key-based partitioning
- Enable retries
- Avoid synchronous blocking
- Compress payloads
Kafka Consumers in Python
Consumers read messages independently and maintain offsets per consumer group, enabling scalable and fault-tolerant processing.
from kafka import KafkaConsumer
import json
consumer = KafkaConsumer(
'orders',
bootstrap_servers='localhost:9092',
auto_offset_reset='earliest',
group_id='order-service',
value_deserializer=lambda x: json.loads(x.decode('utf-8'))
)
for message in consumer:
process_order(message.value)
Key Concepts
- Consumer groups
- Offset commits
- Parallelism via partitions — enabling scalable API platforms and downstream data consumers
- Fault-tolerant processing
Async Kafka Processing with Python
For high-scale systems, asynchronous consumers are preferred to maximize throughput and minimize blocking operations.
from aiokafka import AIOKafkaConsumer
import asyncio
async def consume():
consumer = AIOKafkaConsumer(
'events',
bootstrap_servers='localhost:9092',
group_id='async-group'
)
await consumer.start()
try:
async for msg in consumer:
await handle_event(msg.value)
finally:
await consumer.stop()
asyncio.run(consume())
Used In
- Streaming pipelines for real-time data integration and analytics
- Real-time analytics
- ML feature ingestion
Enterprise Use Cases for Python + Kafka
- Payment & transaction events
- Activity & audit logs
- ETL & ELT pipelines
- IoT telemetry ingestion
- Microservice communication
- AI/ML streaming features
Many of these scenarios rely on event-driven microservices built around Kafka-based messaging
Best Practices for Enterprise Kafka Integrations
Globals break modularity, testability, and concurrency.
- Use schema registry (Avro / Protobuf)
- Enable idempotent producers
- Handle retries & dead-letter topics
- Monitor consumer lag
- Secure Kafka with SSL & SASL
- Separate topics by domain
- Avoid large messages












