Spring Reactive Programming WebFlux —...
December 26, 2025
By Mahipalsinh Rana April 1, 2025
Spring Batch is a lightweight, robust framework designed specifically for high-volume batch processing. Unlike real-time streaming systems, batch jobs prioritize reliability, consistency, and transaction safety when working with large datasets.
For real-time, non-blocking workloads, teams often complement batch systems with reactive architectures such as Spring WebFlux.
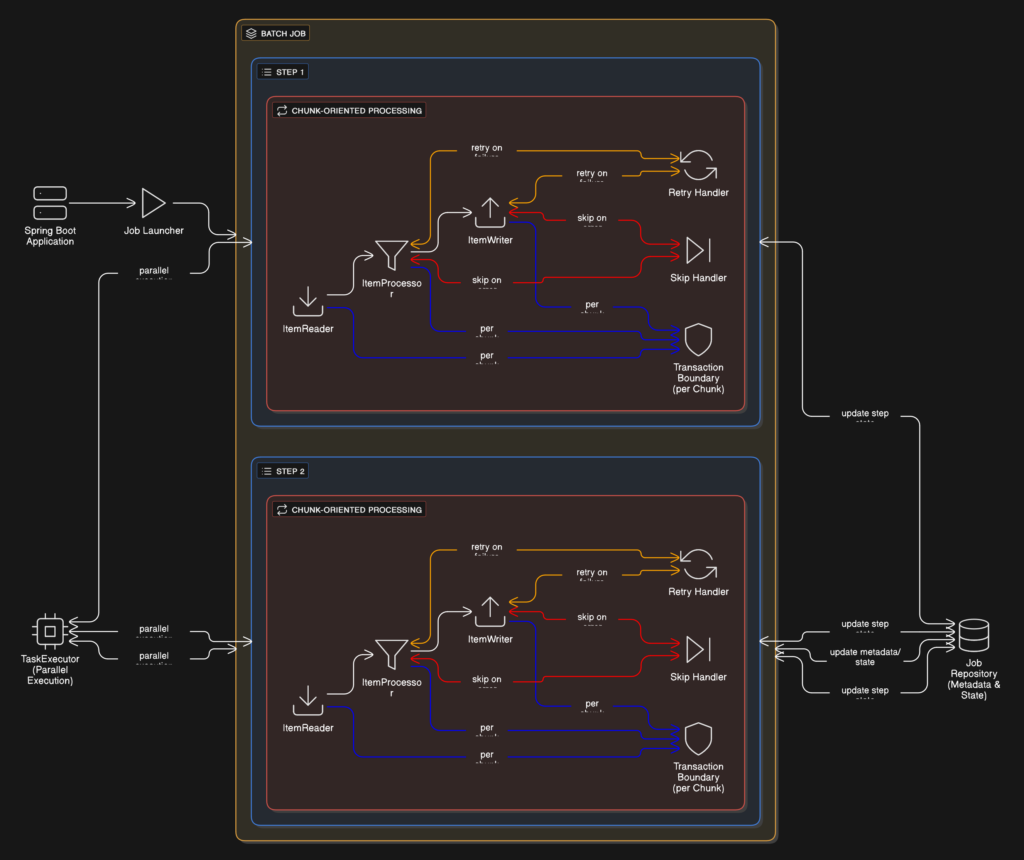
Spring Batch follows a layered execution model:
Designing reliable batch architectures like this is typically handled by experienced backend engineering teams who specialize in transactional systems, orchestration, and fault tolerance.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.batch</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-batch-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-batch</artifactId>
</dependency>
Spring Boot auto-configures the JobRepository, JobLauncher, and required infrastructure, making Spring Batch production-ready out of the box.
.step("importUsers")
.<User, ProcessedUser>chunk(1000)
.reader(userReader())
.processor(userProcessor())
.writer(userWriter())
.build();
@Bean
public Job userJob() {
return jobBuilderFactory.get("userJob")
.start(step1())
.next(step2())
.next(step3())
.build();
}
taskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(10);
taskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(20);
Supported strategies:
Large-scale parallel batch systems are commonly implemented as part of broader Data Engineering & ETL platforms.
.faultTolerant()
.retryLimit(3)
.skipLimit(50)
.retry(SQLException.class)
.skip(ParseException.class)
This ensures batch resilience without manual recovery scripts.
@Scheduled(cron="0 0 1 * * ?")
public void runBatch() throws Exception {
jobLauncher.run(userJob(), new JobParameters());
}
In enterprise environments, these deployment models are automated and governed using Cloud & DevOps pipelines to ensure reliability, observability, and rollback safety.
See how this approach is applied in real-world systems in our Secure File Transfer ETL Pipeline case study.

Written by Mahipalsinh Rana
As the CTO, Mahipalsinh Rana leads with a strategic vision and hands-on expertise, driving innovation in AI, microservices architecture, and cloud solutions. Known for his ability to transform complex ideas into secure, scalable applications, Mahipalsinh has a passion for empowering businesses through cutting-edge technology. His forward-thinking approach and dedication to excellence set the tone for building solutions that are not only impactful but future-ready. Outside the tech sphere, he’s constantly exploring emerging trends, ensuring that his leadership keeps the organization—and its clients—ahead of the curve.
We design scalable, rule-driven enterprise systems using Spring Boot, Drools, Redis, Kafka, and microservices architectures

For 12+ years, Inexture has helped global enterprises design, build, modernize, and scale secure, high-performance digital platforms. We combine deep engineering expertise with cloud, enterprise systems, backend architecture, mobile, AI, and user centric design delivering solutions that make businesses future ready.